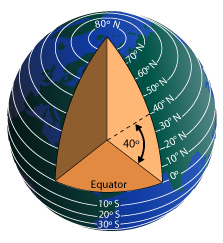
LatitudeDistance north or south from the equator measured in degrees. Notice that they are all the same distance apart. To remember latitude, imagine them as the horizontal rungs of a ladder ("ladder-tude"). 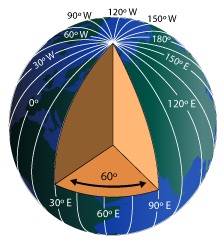
LongitudeDistance measured by degrees or time east or west from the Prime Meridian. Unlike latitude lines, longitude lines are not circular, they begin and end at the poles; they are vertical…and long. To remember longitude, think that the lines are “long dude”. 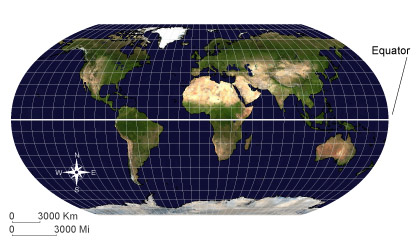
EquatorAn imaginary circle around the center of the earth, equally distant from the North Pole and the South Pole. 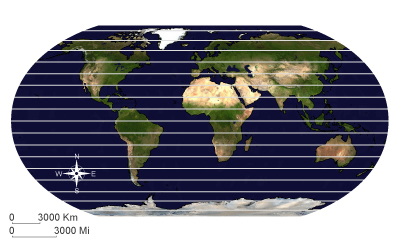
ParallelAny of the imaginary circles around the earth running parallel to the equator and marking latitude. 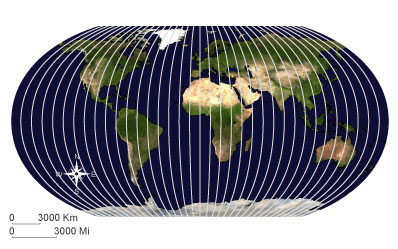
MeridianAny of the imaginary circles around the earth passing through the North Pole and South Pole and marking longitude. 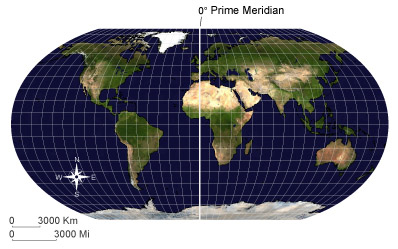
Prime MeridianThe meridian of 0° longitude from which other longitudes are calculated. 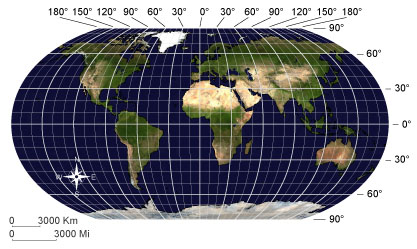
DegreesA unit of measure that identifies latitude and longitude lines. 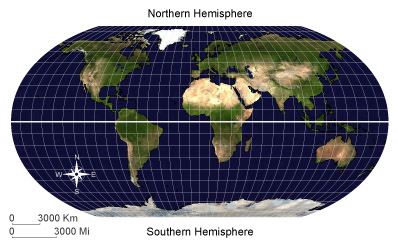
HemisphereOne of the halves of the earth as divided by the equator or by a meridian. 
Compass roseA map element that has arrows that point in all four principle directions: north, south, east, and west. 
LegendA map key. On this map it is designed to show size. ContiguousAdjoining, touching or connected in an unbroken series. Example: In the United States 48 of the states are contiguous, two of the states, Alaska and Hawaii are not physical connected to the other 48 states. Functional regionA region that is made up of different places that are linked and function as a unit. Example: The Washington D.C. metropolitan area is connected by a metro system that allows people to easily move throughout the area. Formal regionAn area or region with features that make it different from surrounding areas. Example: The Sahara Desert has distinct features that set it apart from surrounding areas. Perceptual regionA region that is reflective of human feelings and attitudes. Example: Who we are and where we live affects our perception. For instance, we may not all agree on which states belong to the regions that we call the South or the Midwest. |
About Us | Terms of Use | Contact Us | Partner with Us | Press Release | Sitemap | Disclaimer | Privacy Policy
©1999-2011 OpenLearningWorld . com - All Rights Reserved